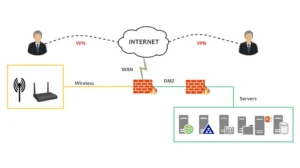
VPNs help create a secure tunnel between your device and a remote server while encrypting your internet traffic. This tunnel has two gatekeepers: the VPN Client and the VPN Server. Both are essential to establishing a VPN connection but have quite a few differences.
Typically, the VPN client initiates the connection with the server but can connect to one server at a time. However, on the server end, there can be multiple established connections. In this article, we shall explore the VPN client vs VPN server battle to learn more about their respective roles.
Do I Need a VPN Server or Client?
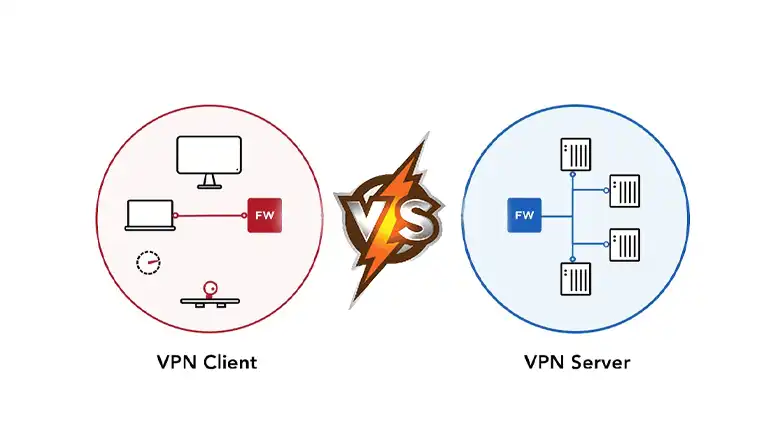
Both VPN client and server are essential. If either is missing, the VPN won’t work as intended. You cannot connect to the server without having the client application installed on your device. And without the server, there’s technically no service provider.
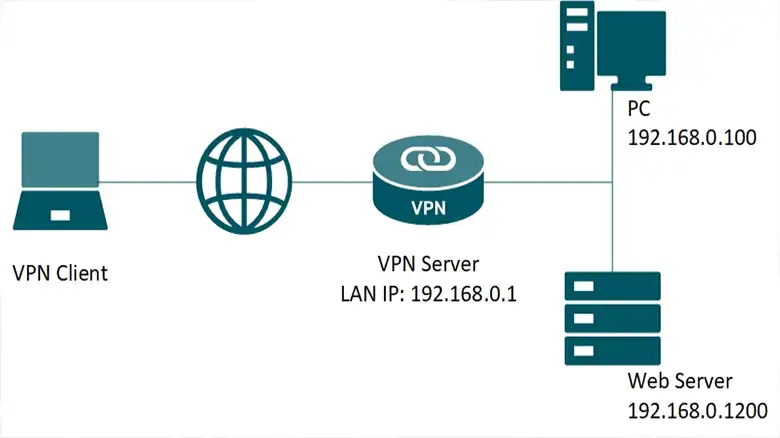
Why Use a VPN Client?
A VPN client is generally a software application that runs on an end user’s computer and initiates the connection to a VPN server. It is the user’s entry point into the VPN network and is responsible for encryption, authentication, and IP address masking.
User Authentication and Establishing Connection
When launching the VPN client, you must provide credentials, such as a username and previously shared encryption key. The keys used by the client should match those used on the server end.
Once authenticated, the client establishes a secure connection with the VPN server. There’s generally strong encryption in place to protect your online activities from malicious third-party actors.
Data Encryption
Data transmitted between your device and the VPN server goes through encryption provided by the client software. Therefore, your data remains unreadable even if intercepted on the way to the server.
Masking IP
The VPN client’s responsibility is to assign a new IP address provided by the VPN server to your device. That way, it hides your original IP address and makes you somewhat anonymous to internet services.
Note that a VPN client can also be a separate hardware device, often used to provide site-to-site VPN connections.
Why Use a VPN Server?
Unlike VPN clients, VPN servers are remote machines or networks of hardware that receive, decrypt, and forward data traffic between the client and the internet. It acts as a central hub of a VPN network and provides the following functionalities.
User Traffic Routing
When you initiate a VPN connection through your VPN client, the VPN server routes your internet traffic through its secure network. It then redirects your traffic to its final destination on the untrusted internet. This process helps keep your data safe and anonymous.
Data Decryption
A VPN server decrypts the incoming data packets encrypted from the client end and sends it to the receiver.
Providing IP Addresses
The VPN server assigns IP addresses to connected clients and hides the actual IP address of the client. This masking process adds a layer of anonymity to your online presence while safeguarding your location and identity.
Load Balancing
VPN servers often use load-balancing techniques to distribute traffic during heavy usage or multiple simultaneous connections. As a result, the overall responsiveness of the VPN network remains constant.
You can implement VPN servers through software solutions, but the process is often very complex.
VPN Client vs VPN Server: Key Differences
Here are the major differences between a VPN client and a VPN server in a nutshell.
| Aspect | VPN Client | VPN Server |
| Role in VPN Network | User’s gateway into the VPN network | Central hub for routing, decryption, and traffic management |
| Purpose | Initiates secure connections to VPN servers | Accepts incoming connections from clients and manages traffic |
| Data Encryption/Decryption | Encrypts user’s data traffic before transmission | Decrypts incoming data packets from clients |
| Number of Connections | Typically handles a single user’s connection | Handles multiple simultaneous connections from multiple clients |
| Location | User end | Data centers or cloud |
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a VPN work without a server?
The short answer is no. A VPN only works when connected to a remote VPN server.
Should you use a VPN extension or the client app?
Whether to use a VPN extension or a client application depends on your desired level of protection. Although both provide protection, we recommend considering a full-fledged app over a browser extension if you want the safest connection.
Does it matter what VPN client you use?
It does not matter as long as your VPN provider supports VPN protocol switching. Protocols used on the client and server should match.
Conclusion
Understanding these differences between VPN clients and VPN servers can help you make informed decisions when selecting, configuring, and managing your VPN services. And we hope this article has provided just that, a clear understanding. After all, a secure online presence is your right. Thanks for reading!