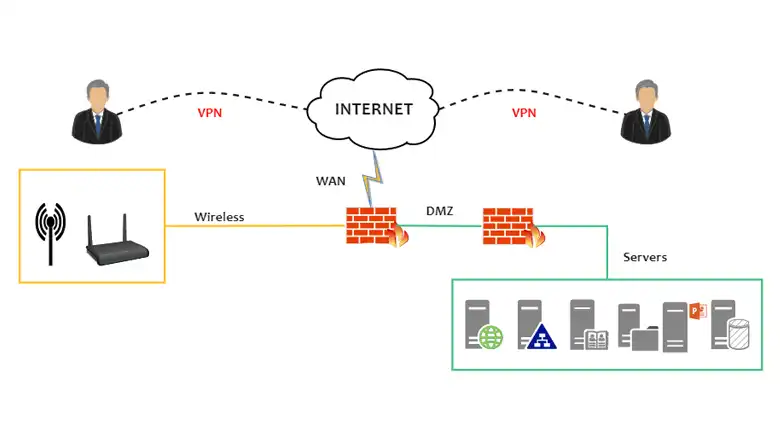
A DMZ (Demilitarized Zone), sometimes known as a perimeter network, is a subnetwork that isolates public-facing services from the internal network. In contrast, a VPN (Virtual Private Network) is a technology used to provide secure, encrypted communication while ensuring data privacy.
So, a DMZ is different from a VPN and you cannot use them interchangeably. In this article, we’ll discuss that in detail and help you understand the differences between a DMZ and a VPN. Stay tuned till the end so you can choose which to use and when.
Are DMZs the Same as VPNs?
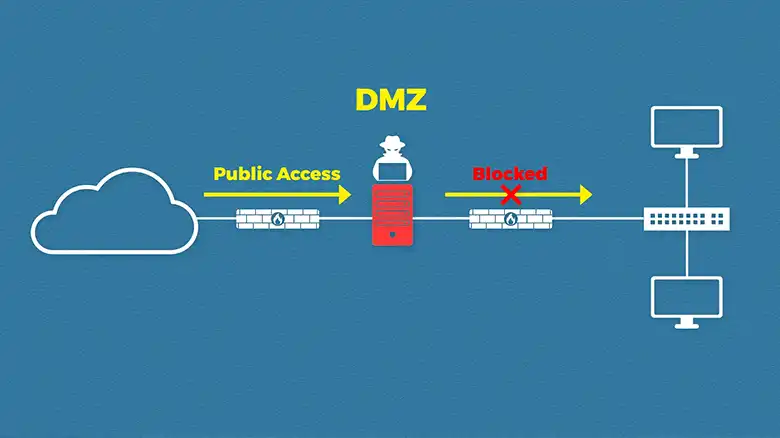
A Demilitarized Zone, commonly referred to as a DMZ, is a network architecture that segregates a portion of a network from the internal network and the external internet. It acts like a buffer zone between users from the untrusted network and services behind the firewall.
The purpose of a DMZ is to create an isolated environment for services accessible to the end user. A company’s email servers, web servers, and DNS servers are examples of such public-facing services. These servers are, therefore, placed in the DMZ.
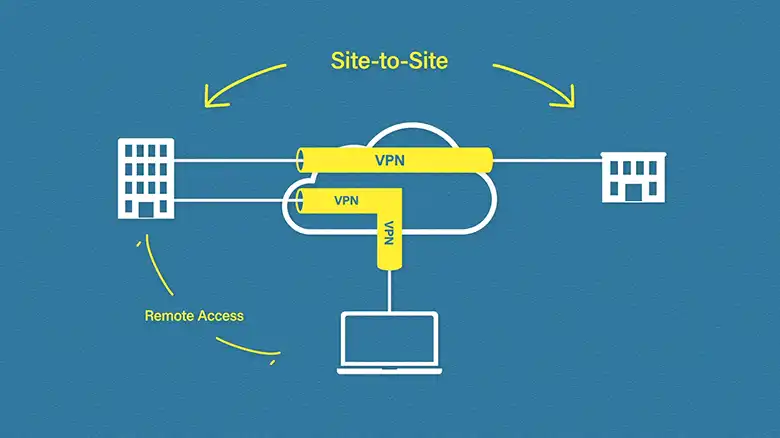
On the other hand, a VPN means establishing an encrypted network tunnel between a user and a remote network, often over the public internet. Though it sounds similar to a DMZ, a VPN works on the user end to protect their online activities from third parties.
A VPN uses remote servers as hosts to redirect your online traffic, effectively hiding your location and browsing history. It replaces your IP address with the server IP to make you somewhat anonymous to web services, including your ISP.
DMZ vs VPN: What’s the Difference?
Since DMZs and VPNs are not the same, they must have some fundamental differences. Here’s a summary of the key differences between them.
| Aspect | DMZ | VPN |
| Purpose | Acts as an isolated network segment to host public-facing servicesEnhances Security by providing a buffer zone between the internal and external network | Provides secure, encrypted connection between end users and a remote networkEnsures privacy and secure access to resources |
| Isolation | Isolated (physically or logically) from the internal network to safeguard important resources. | Allows for secure communication over potentially untrusted networks. |
| Security Measures | Uses firewalls and intrusion detection systems to detect and prevent threats. | Uses encryption to create a safe data transmission tunnel. |
| Use Cases | Hosting public services like web and email servers. | Providing secure access for remote employees. |
| Location | Physically located within an organization’s network infrastructure. | VPN servers may be located at different geographical locations. |
Frequently Asked Questions
Is VPN server in DMZ?
You can place a VPN server in a DMZ, but the decision will depend on the network architecture and security requirements. Such a configuration has both advantages and disadvantages. While it may enhance the security, there can be performance constraints and other complexities.
Does a DMZ have an IP address?
A DMZ may have one or more IP addresses assigned to the devices and servers within it. These are usually public IP addresses so that the services in the DMZ are accessible directly from the internet.
Is DMZ a security zone?
A DMZ network works as a network segment, home to the outward-facing services of a company, such as email and SMTP servers. Despite being exposed to the internet, it saves internal resources from potential threats.
Final Verdict
In conclusion, a DMZ is not the same as a VPN. They have separate roles, but if combined and applicable, they can provide a robust defense against online threats to an organization. We hope this article clarifies the differences between a DMZ and a VPN. If you have any questions or comments, please share them below. Thank you for reading!


![Read more about the article [2 Fixes] AnyConnect Is Not Enabled on The VPN Server | A Solving Guideline for You](https://vpnaware.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/03/AnyConnect-Is-Not-Enabled-on-The-VPN-Server-300x168.webp)